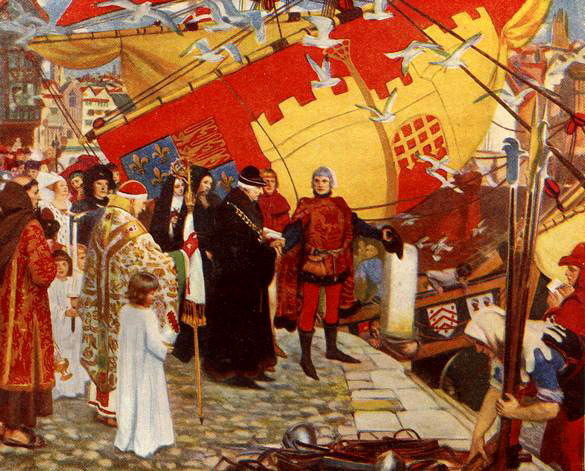
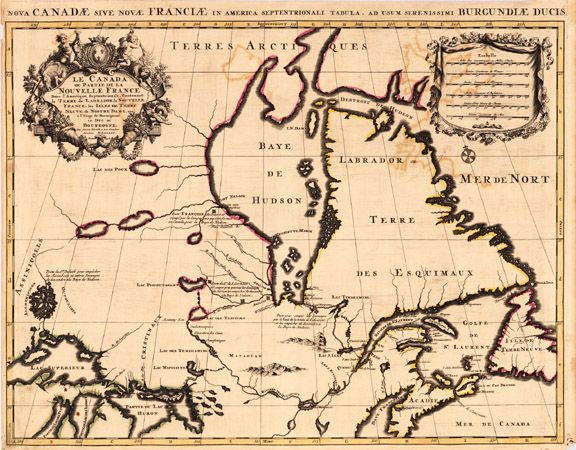
The first known attempt at European colonization began when Norsemen settled briefly at L’Anse aux Meadows in Newfoundland around 1000 AD. No known European exploration occurred again until 1497, when Italian seafarer John Cabot discovered Newfoundland’s Grand Banks for England. Basque and Portuguese mariners soon established seasonal whaling and fishing outposts along the Atlantic coast in the early 16th century. In 1534, French explorer Jacques Cartier explored the St. Lawrence River, where on July 24 he planted a 10-metre (33 ft) cross bearing the words “Long Live the King of France”, and took possession of the territory in the name of King Francis I of France.
In 1583, Sir Humphrey Gilbert claimed St. John’s, Newfoundland, as the first North American English colony by the royal prerogative of Queen Elizabeth I. French explorer Samuel de Champlain arrived in 1603, and established the first permanent European settlements at Port Royal in 1605 and Quebec City in 1608. Among the French colonists of New France, Canadiens extensively settled the St. Lawrence River valley and Acadians settled the present-day Maritimes, while fur traders and Catholic missionaries explored the Great Lakes, Hudson Bay, and the Mississippi watershed to Louisiana. The Beaver Wars broke out in the mid-17th century over control of the North American fur trade.
The English established additional colonies in Cupids and Ferryland, Newfoundland, beginning in 1610. The Thirteen Colonies to the south were founded soon after. A series of four French and Indian Wars erupted between 1689 and 1763. Mainland Nova Scotia came under British rule with the 1713 Treaty of Utrecht; the Treaty of Paris (1763) ceded Canada and most of New France to Britain after the Seven Years’ War.
The Royal Proclamation of 1763 created the Province of Quebec out of New France, and annexed Cape Breton Island to Nova Scotia. St. John’s Island (now Prince Edward Island) became a separate colony in 1769. To avert conflict in Quebec, the British passed the Quebec Act of 1774, expanding Quebec’s territory to the Great Lakes and Ohio Valley. It re-established the French language, Catholic faith, and French civil law there. This angered many residents of the Thirteen Colonies, fuelling anti-British sentiment in the years prior to the 1775 outbreak of the American Revolution.
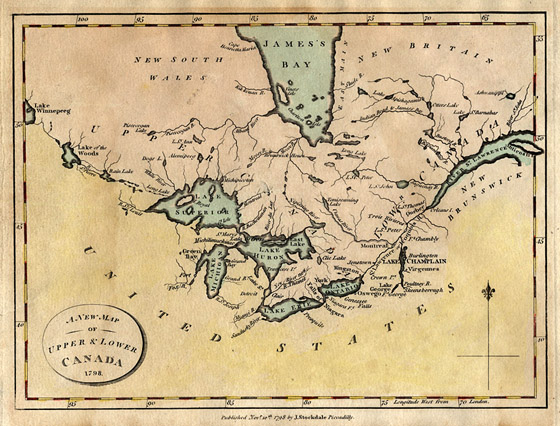
The 1783 Treaty of Paris recognized American independence and ceded territories south of the Great Lakes to the United States. New Brunswick was split from Nova Scotia as part of a reorganization of Loyalist settlements in the Maritimes. To accommodate English-speaking Loyalists in Quebec, the Constitutional Act of 1791 divided the province into French-speaking Lower Canada (later Quebec) and English-speaking Upper Canada (later Ontario), granting each its own elected legislative assembly.
The Canadas were the main front in the War of 1812 between the United States and Britain. Following the war, large-scale immigration to Canada from Britain and Ireland began in 1815. Between 1825 and 1846, 626,628 European immigrants reportedly landed at Canadian ports. Between one-quarter and one-third of all Europeans who immigrated to Canada before 1891 died of infectious diseases.
The desire for responsible government resulted in the abortive Rebellions of 1837. The Durham Report subsequently recommended responsible government and the assimilation of French Canadians into English culture. The Act of Union 1840 merged the Canadas into a united Province of Canada. Responsible government was established for all British North American provinces by 1849. The signing of the Oregon Treaty by Britain and the United States in 1846 ended the Oregon boundary dispute, extending the border westward along the 49th parallel. This paved the way for British colonies on Vancouver Island (1849) and in British Columbia (1858).
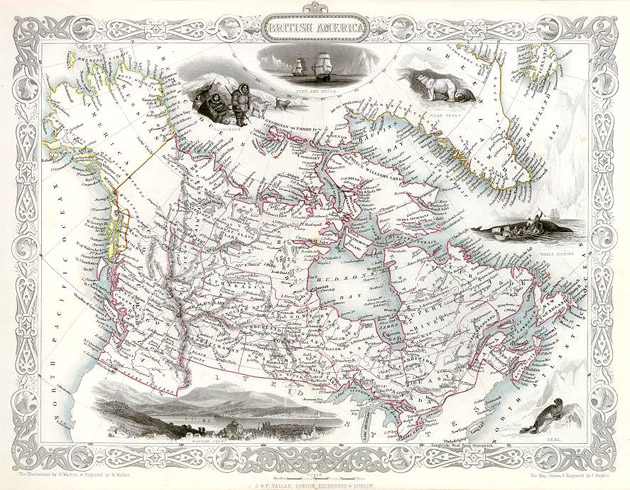
Following several constitutional conferences, the 1867 Constitution Act officially proclaimed Canadian Confederation on July 1, 1867, initially with four provinces – Ontario, Quebec, Nova Scotia, and New Brunswick. Canada assumed control of Rupert’s Land and the North-Western Territory to form the Northwest Territories, where the Métis’ grievances ignited the Red River Rebellion and the creation of the province of Manitoba in July 1870. British Columbia and Vancouver Island (which had been united in 1866) joined the Confederation in 1871, while Prince Edward Island joined in 1873. Prime Minister John A. Macdonald and his Conservative government established a National Policy of tariffs to protect the nascent Canadian manufacturing industries.
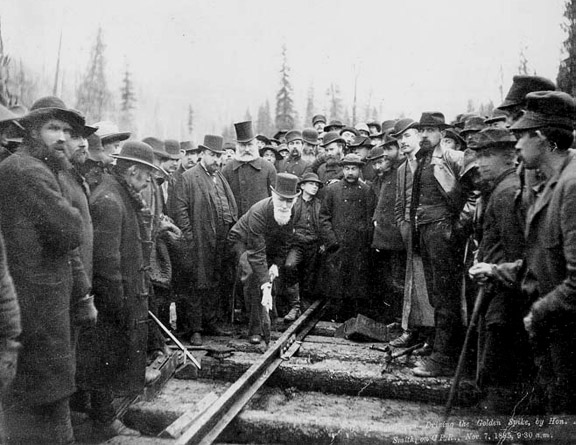
To open the West, the government sponsored the construction of three transcontinental railways (including the Canadian Pacific Railway), opened the prairies to settlement with the Dominion Lands Act, and established the North-West Mounted Police to assert its authority over this territory. In 1898, during the Klondike Gold Rush in the Northwest Territories, the Canadian government created the Yukon Territory. Under the Liberal Prime Minister Wilfrid Laurier, continental European immigrants settled the prairies, and Alberta and Saskatchewan became provinces in 1905.
Because Britain still maintained control of Canada’s foreign affairs under the Confederation Act, its declaration of war in 1914 automatically brought Canada into World War I. Volunteers sent to the Western Front later became part of the Canadian Corps. The Corps played a substantial role in the Battle of Vimy Ridge and other major engagements of the war. Out of approximately 625,000 Canadians who served in World War I, around 60,000 were killed and another 173,000 were wounded. In 1919, Canada joined the League of Nations independently of Britain, and the 1931 Statute of Westminster affirmed Canada’s independence. The Dominion of Newfoundland (now Newfoundland and Labrador) joined Canada in 1949.
Text Source: Wikipedia